For decades, the idea of humanoid robots has captivated the human imagination. From science fiction classics to modern blockbusters, these robots, designed to resemble humans in form and function, have consistently pushed the boundaries of our technological aspirations and anxieties. Today, the dream of creating true humanoids is closer than ever, with rapid advancements in robotics, artificial intelligence, and computer vision driving this exciting field forward.
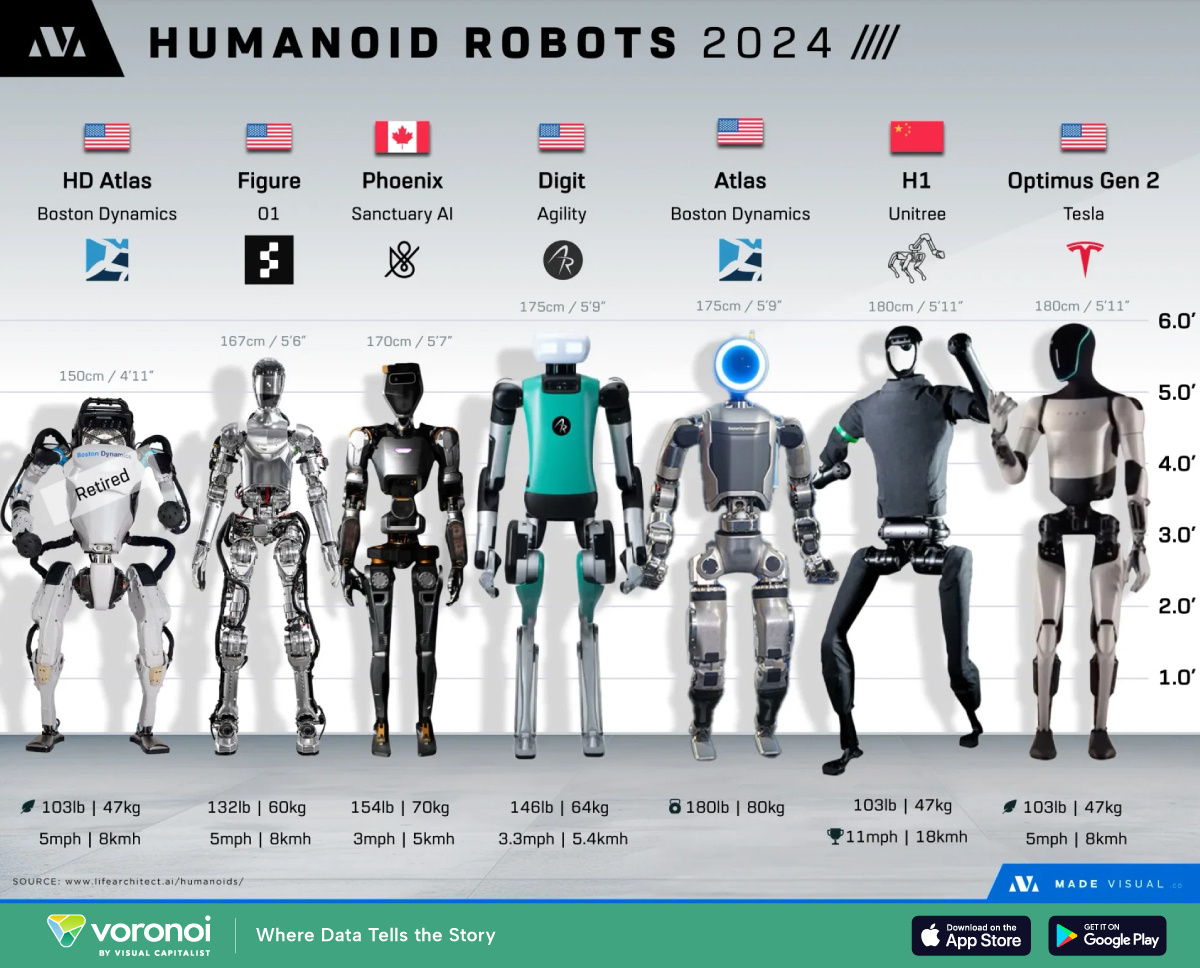
The Driving Forces Behind Humanoid Robotics
The development of humanoid robots is fueled by a confluence of factors:
- Scientific Curiosity: Understanding the complexities of human movement and cognition remains a driving force for researchers. Building robots that mimic these aspects allows for deeper insights into both human and artificial intelligence.
- Automation and Labor: Humanoid robots offer the potential to automate tasks requiring dexterity, adaptability, and complex decision-making in challenging environments. Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and disaster relief could benefit significantly from such capabilities.
- Accessibility and Service: Imagine robots that can assist with everyday tasks like household chores, personal care, or companionship for the elderly and disabled. Humanoid robots, designed to interact naturally with humans, could revolutionize how we live and work.
- Exploration and Research: Deploying humanoid robots in dangerous or inaccessible locations like deep-sea exploration or space exploration can provide valuable data and insights without putting human lives at risk.
The Building Blocks of Humanoids
Creating a humanoid robot is a multidisciplinary endeavor, requiring expertise in various fields:
- Mechanics and Engineering: Designing sturdy, lightweight structures capable of replicating human movement and balance is crucial. Actuators (motors), sensors, and joints must work seamlessly to enable natural and fluid motion.
- Control Systems:
Sophisticated algorithms are needed to process sensory information, make decisions, and control the robot’s movements. These systems must be robust and adaptable to unpredictable environments.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Giving humanoid robots cognitive abilities, such as object recognition, language comprehension, and problem-solving, requires advanced AI techniques. Machine learning and deep learning play a vital role in enabling robots to learn from data and improve their performance over time.
- Human-Robot Interaction (HRI): Designing for natural and intuitive interaction with humans is essential for building trust and facilitating collaboration. This involves considering factors like voice recognition, gesture interpretation, and emotional cues.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite significant progress, developing truly human-like robots remains a formidable challenge. Key hurdles include:
- Dexterity and Manipulation:
Replicating the fine motor skills and dexterity of human hands is incredibly complex.
- Cognitive Abilities: Achieving human-level intelligence, including common sense reasoning, creativity, and emotional understanding, is a grand challenge in AI research.
- Safety and Reliability: Ensuring that humanoid robots operate safely and reliably in shared environments with humans is paramount.
Beyond technical challenges, ethical considerations surrounding humanoid robots are crucial:
Job displacement: As robots become more capable, concerns arise about their impact on human employment.
Privacy and security: Data collected by humanoid robots raises concerns about privacy and potential misuse.
Bias and discrimination: If trained on biased data, robots could perpetuate societal prejudices and inequalities.
The Future of Humanoid Robots
The development of humanoid robots is a journey filled with both promise and perils. While widespread humanoid robots assisting in everyday life might still be some years away, the advancements we see today pave the way for a future where human-robot collaboration becomes increasingly prevalent.
Navigating the ethical challenges responsibly and ensuring that these technologies benefit all of humanity will be crucial to shaping a future where humans and robots coexist harmoniously.
FAQ
Q: What are some examples of existing humanoid robots?
A: Some notable examples include:
- ASIMO (Honda): A highly advanced humanoid robot capable of walking, running, and performing complex tasks.
- Sophia (Hanson Robotics): A social humanoid robot known for its realistic facial expressions and ability to engage in conversation.
- Atlas (Boston Dynamics): A highly agile and dynamic robot capable of navigating complex terrain and performing impressive acrobatic feats.
Q: What is the difference between a humanoid robot and a traditional industrial robot?
A: Traditional industrial robots are typically designed for specific tasks in factories and manufacturing settings. They are often stationary, lack human-like mobility, and are primarily focused on repetitive tasks. Humanoid robots, on the other hand, are designed to resemble humans in appearance and movement, enabling them to interact with the world in a more versatile and adaptable manner.
Q: Will humanoid robots replace human jobs?
A: It’s difficult to say definitively. While robots can automate certain tasks, they are unlikely to completely replace humans in complex jobs requiring creativity, critical thinking, and social intelligence. However, some jobs may be transformed or require new skillsets as robots take over routine or physically demanding tasks.
Conclusion:
Humanoid robots represent a fascinating intersection of technology, science, and ethics. As development continues, we can expect these robots to play an increasingly significant role in our lives, offering both exciting opportunities and complex challenges. Navigating this evolving landscape responsibly will be essential to ensuring that humanoid robots benefit humanity as a whole.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Rise of the Machines: A Look at Humanoid Robot Development. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
